- Whenever you access the Internet, your device transmits (sends and receives) data units called packets.
- When some of those packets fail to reach their destination, we call it packet loss.
- If you're looking for more information about digital tools, visit our Software page.
- Visit our Network & Internet Hub to learn more about managing your network like a pro.

Compared to a few years ago, the structure of networks has become very complex in nature. In order to increase security, speed, and efficiency, the use of specific protocols has become a necessity.
However, one thing hasn’t changed, and that’s the annoying phenomenon of losing data packets.
Due to various factors, your network might be subject to various disturbances, which often lead to high ping situations and even packet loss.
What is packet loss?
Whenever you access the Internet, your device transmits (sends and receives) data units called packets. If some of those packets fail to reach their destination, we call it packet loss.
This phenomenon can be observed through network slowdowns, disruptions, and even total network connectivity loss.
Although any network service can be targeted by packet loss, it appears that games, VoIP services, as well as multimedia streaming services are more affected.
The reason why these types of apps are more likely to suffer from packet loss is that they process packets in real-time.
What causes packet loss?
- An overloaded network: high traffic volume over several devices such as routers, servers, and terminals.
- Unstable devices: if some of the devices on your network have weak or overloaded CPUs, said devices become unable to process data entirely. This can affect your whole network and be a cause of packet loss.
- Software/firmware issues: glitches in a network device’s software can lead to packet loss, which can affect the whole network.
- Hardware-related issues: low-quality cables, faulty RAM module, outdated network adapter, these can all contribute to causing packet loss.
There are many factors that can play a role in packet loss occurring on your connection. However, the ones above are among the most common ones.
How to test for packet loss?
1. Use specialized software such as PRTG Network Monitor
- Download PRTG and install it on your PC
- Wait for the installation to complete (takes a while)
- Launch PRTG and log into it
- Let it perform the initial assessment and create sensors for your network devices
- Observe any faults or malfunctions with your network devices (high ping/packet loss)
PRTG Network Monitor is a complex tool that can perform an extensive analysis of your network and its devices.
Some PC users might still consider it intimidating from a feature standpoint, but it offers an interactive tutorial as soon as you log into it, so you will be just fine.
Its (web) interface comes with a broad range of tools you can work with and even define your own sensors.
For instance, you can stay protected by using the built-in Packet Sniffing Sensor that detects suspicious network packets.
You’ll be glad to know that it has a general trial. During the trial, you can use the app with unlimited sensors (30 days).
After the trial expires, you’ll be limited to 100 sensors.

PRTG Network Monitor
Forget about packet loss and other network problems! Use the best network monitoring tool on the market for your PC!
2. Use Windows’ built-in set of tools
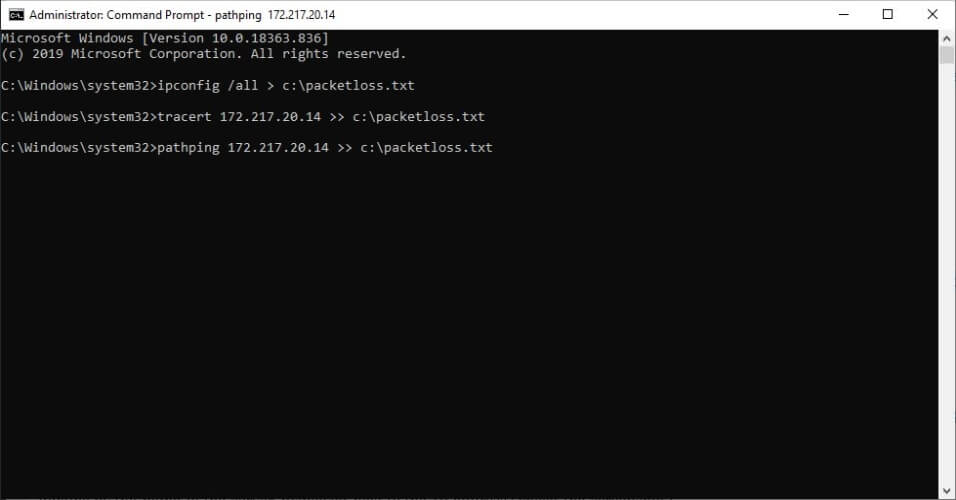
- Use a packet sniffer such as Wireshark to see what servers you’re connected to
- Hit the Win key on your keyboard and type cmd
- Right-click the Command Prompt and select Run as administrator
- Type the following line in Command Prompt:
ipconfig /all > c:packetloss.txt - Now type the following line and replace x.x.x.x with the IP of the server you suspect of packet loss:
tracert x.x.x.x >> c:packetloss.txt - Type the following line and replace x.x.x.x with the IP of the server you suspect of packet loss:
pathping x.x.x.x >> c:packetloss.txt - Wait for the pathping operation to complete (can take up to 10 minutes)
- Check the created file for high ping values, which can signal packet loss
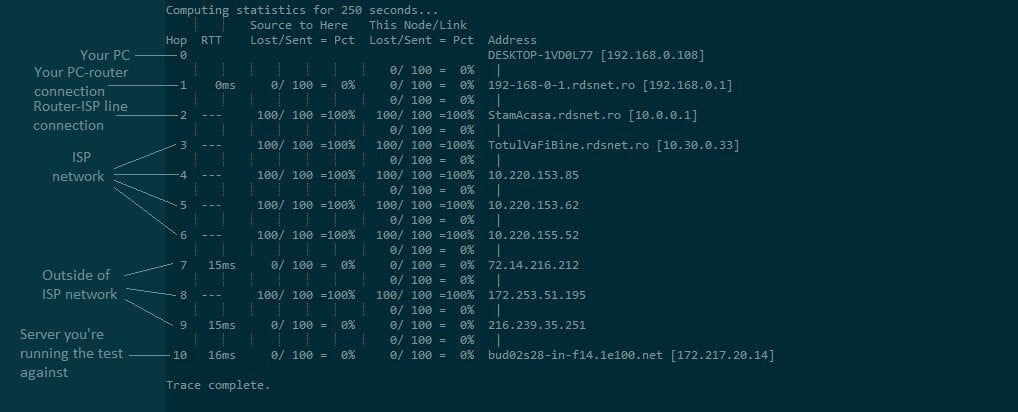
As hop count increases, your connection gets further away from your PC.
Therefore, the first hop (i.e. hop 0) is your PC, the next hop (hop 1) is your PC-router connection, hop 2 is the connection from your router to your ISP’s line.
After the third hop (hop 2), the connections belong to your ISP’s network.
You should be able to single out the owner of the server judging by the name of the server displayed next to the IP address (check the screenshot).
The last hop is the server you connected to and ran the test against.
Note: If you don’t want to create any log file on your PC (i.e. the packetloss.txt document), you can run the commands listed above without the > C:packetloss.txt and >> c:packetloss.txt bits.
Doing so will only display results in the command prompt.
How to fix packet loss?
1. Use a VPN
Using a VPN such as Kape Technologies’ Private Internet Access can help you improve ping and thus curb packet loss, especially if your ISP throttles your connection.
PIA re-routes all of your traffic through its private network of servers, and if your ISP has bad routing, your packet loss issue will likely be fixed.
Not only can this service improve your ping, but it can also protect your privacy, keep your connection secure, away from prying eyes, and lift geo-restrictions for you by spoofing your location.

Private Internet Access
PIA can help you solve packet loss issues and improve your ping while protecting your privacy at the same time.
2. Isolate and troubleshoot each hop

Therefore, you need to isolate the issue and understand what part of your connection is exactly at fault.
Therefore, the first step would be checking the log file you created earlier or the results in the command prompt window.
There are 5 different scenarios and we’re going to discuss each and every one of them.
High ping on hop 0 and/or hop 1

You need to check that you’re using high-quality Ethernet cables, or, if you’re using Wi-Fi, try using a wired connection and run the test again, to see if there’s any improvement.
Hard-reset your router, and maybe check the configuration of your PC’s network adapter. You need to check every single component between your PC and router carefully, including the two ends of that connection (i.e. your PC and your router).
High ping on hop 2

Therefore, if there’s nothing wrong with your router, then it might be the cable that belongs to your ISP, and goes into the WAN port of your router.
In this case, you might want to give your ISP a call and ask them if there seems to be a problem on their side.
High ping on your ISP hops (e.g. 3, 4, 5)

Remember that neither tracert or pathping is illegal to use, so don’t be shy and offer your ISP as many details as you can. Your information might be of great value to the support team.
If the high ping is outside of your ISP network you also need to call your ISP and tell them about your findings. Maybe they’ll know how to tackle this situation onward.
High ping at the last hop
The last hop stands for the server you’ve connected to and running your tests against.
Therefore, if you notice high ping exclusively on this hop, there’s nothing wrong on your side and the server is clearly experiencing some problems.
If you want to, you can contact the service you’re having trouble with and make them aware of the situation.
For instance, if it’s a game server, try contacting the game’s support crew and tell them about your findings.
Packet loss can sometimes be reduced

Sure, it’s annoying and renders your connection unusable at times, but if you have a bit of patience, you can figure out where the problem is and maybe even fix it.
FAQ: Learn more about packet loss
Yes, but it’s not a given. The short answer is that if your ISP is generally awful and has a bad routing, a VPN such as PIA can definitely improve your ping, and also curb packet loss dramatically.
A lot of factors can play major roles in the occurrence of packet loss. Some of them include the overloading of the network, poorly configured (routed) networks, as well as hardware and software errors.
- Can a bad Ethernet cable cause packet loss?
Definitely yes. If you’re using old, damaged, slow, or improperly wired Ethernet cables, they will likely leak packets. Also, a poorly configured Wi-Fi router can cause packet loss, so make sure to keep a close eye on your setup.
Editor’s Note: This post was originally published in May 2020 and has been since revamped and updated in August 2020 for freshness, accuracy, and comprehensiveness.
Thank you for viewing the article, if you find it interesting, you can support us by buying at the link:: https://officerambo.com/shop/
No comments:
Post a Comment